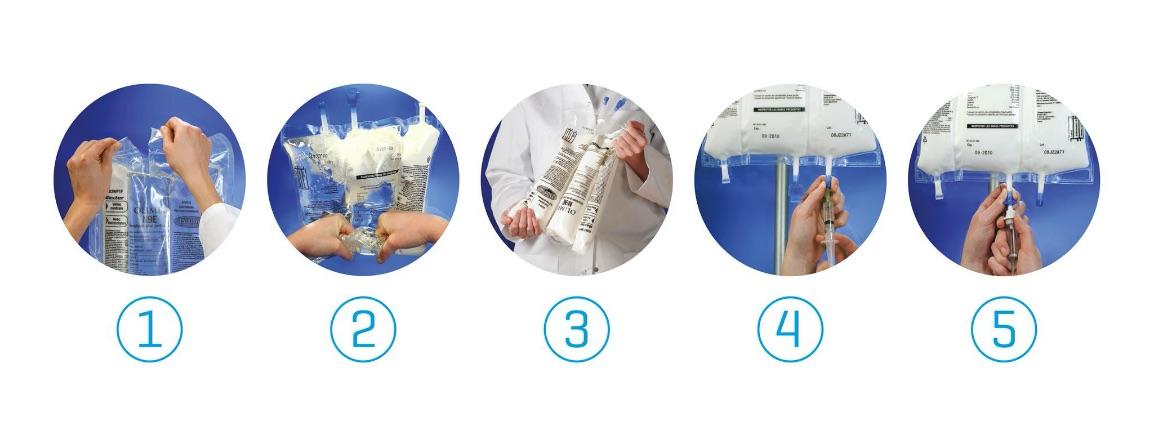
Olimel
The Olimel portfolio gives you the broadest selection of three-chamber bags with an olive oil-based lipid to meet the unique nutrition needs of each patient.

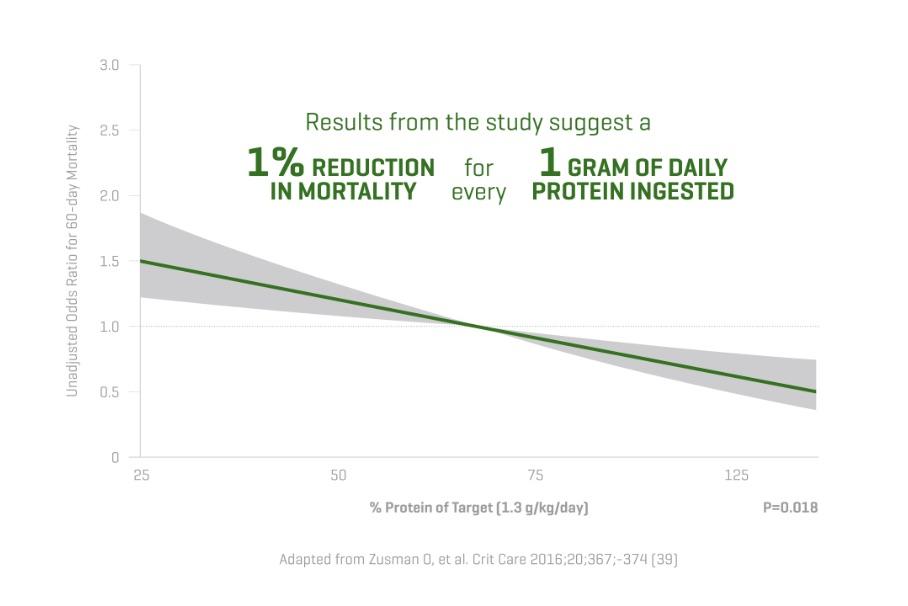
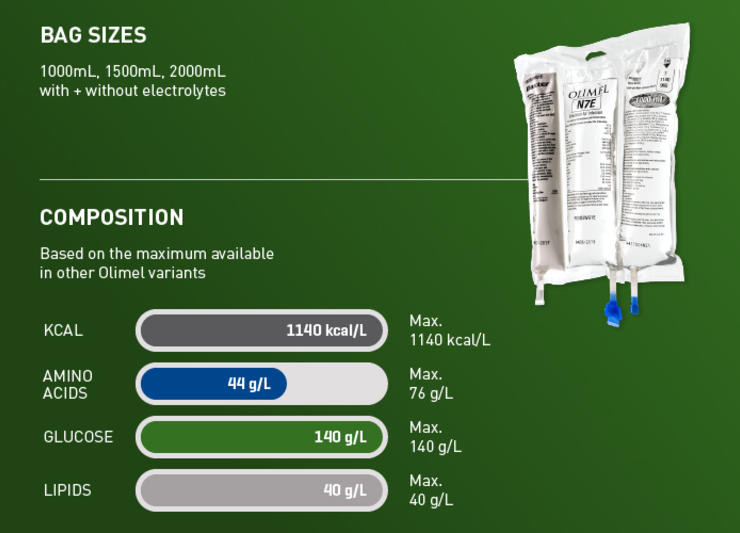
Not all critically ill patients are the same, and neither are their nutritional requirements. The Olimel portfolio offers a range of central and peripheral formulations to match the individual protein and energy needs of your patients.1-3 Olimel N12 combines a high protein formulation with low glucose content, resulting in the lowest energy to protein ratio currently available in a standardized, three-chamber bag (3CB).2,3,18-23 Olimel contains olive oil, which is rich in long-chain Omega-9 monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), with fewer polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) than soybean and fish oil.26 An olive oil-based lipid emulsion may preserve immune function and has been associated with fewer infections than soybean oil.4,10-12
See full prescribing information for Olimel N12 SmPC
See full prescribing information for Olimel N12E SmPC
See full prescribing information for PeriOlimel N4 & Olimel N5, N7, N9 SmPC
Olimel - meeting the unique nutritional needs of each patient

Preserve immune function
Olimel contains an olive oil-based lipid emulsion, which is associated with fewer infections and may preserve immune function.4,10-12

Reach protein targets with less fluid
Olimel N12 combines a high protein formulation with low glucose content, resulting in the lowest energy to protein ratio currently available in a standardized 3CB.2,3,18-23

Personalize without compromise
Broadest selection of 3CBs to meet the unique nutrition needs of each patient.1-3

Reduce risk of hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is associated with an increased risk of infections.15-19 With only 73 g/L, Olimel N12 has one of the lowest glucose levels available in a 3CB.2,3,18-23